Your Child's Nasogastric Tube: Flushing the Tube
Your child is going home with a nasogastric (NG) feeding tube in place. This is a soft, thin tube put in through your child’s nose that goes down into the stomach. It sends liquid food directly to the stomach. You’ll need to flush your child’s tube regularly to keep it from getting clogged. You were shown how to do this before your child left the hospital. This sheet will help you remember those steps at home. If you need more help, talk with the hospital staff. They can tell you how to arrange for a home health nurse to help you.
Keep in mind that there are many types of NG tubes and syringes. Your child’s NG tube and supplies may look or work differently than those shown here. One type of tube has a connection that lets you plug or push the syringe into the NG tube port. Another type has a twist-on safety connector. The twist-on safety connector means you must use a certain type of syringe. This twists onto your child's NG tube port. Follow your child's care team's directions for your child's NG tube.
Note
Take care to keep the feeding tube from becoming a strangulation risk to your child. Follow your healthcare team's advice on how to secure the tube safely.
Contact information to keep handy
Ask for phone numbers to call if you need help. Also have the phone number for your child’s medical supply company. You’ll need to order more supplies for your child in the future. Write all of these phone numbers below.
Healthcare provider phone number:
Home health nurse phone number:
Medical supply company phone number:
Flushing the tube for bolus feeding using a syringe
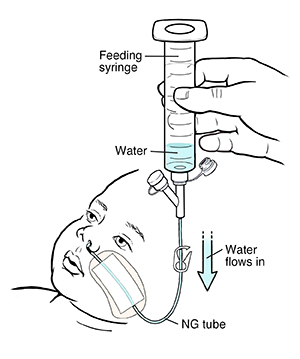
Flush your child’s NG tube after each feeding, or as directed by your child’s healthcare provider or home health nurse.
The supplies you'll need are:
Follow these steps:
-
Wash your hands with soap and clean, running water for at least 20 seconds. Dry them with a clean towel.
-
Make sure the feeding syringe is connected to the NG tube.
-
Pour water into the syringe. If there is a clamp on the tubing, make sure it is open. Let the water run through the NG tube by gravity.
-
If the water flows too slowly or doesn’t flow at all, place the plunger in the syringe. Gently push the plunger a small amount. This can help remove anything that is blocking or clogging the NG tube. Don't push hard. And don't push the plunger all the way into the syringe. Changing your child’s position so that they are lying down or sitting upright may also improve the flow.
-
If there is a clamp on the tubing, close it once all the water has flowed through the tube.
-
Disconnect the syringe from the NG tube when the flushing is done.
-
Close the feeding port cap of the NG tube.
Other instructions:
Flushing the tube for bolus feeding or continuous feeding using a pump
Flush your child’s NG tube after each bolus feeding, or as directed by your child’s healthcare provider or home health nurse. With continuous feeding, you may only need to flush the tube after the last daily feeding. Follow your child's healthcare team's specific instructions.
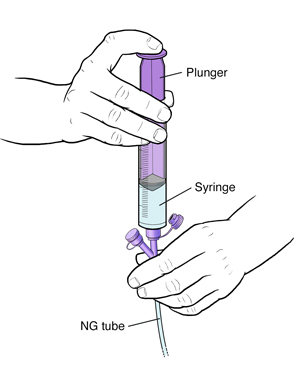
The supplies you’ll need are:
Follow these steps:
-
Wash your hands with soap and clean, running water for at least 20 seconds. Dry them with a clean towel.
-
Make sure the pump is in the STOP/OFF mode.
-
Not all tubes have clamps. If the tubing has a clamp, make sure the clamp on the feeding bag tubing is closed.
-
Disconnect the feeding bag tubing from the NG tube.
-
Put the tip of the empty syringe in water.
-
Draw up 1 to 5 ml (cc) of water. Follow your child's healthcare provider's instructions on how much water to use. The amount will vary by your child's age, needs, and situation.
-
Connect the syringe to the feeding port of the NG tube. Depending on the type of NG port your child has, you may plug in the syringe or twist it on. If the NG tube has a clamp make sure it is open.
-
Gently push the plunger all the way into the syringe. If there is a clamp on the NG tube, close it once all the water has been pushed out of the syringe.
-
Disconnect the syringe from the NG tube when the flushing is done.
-
Close the feeding port cap of the NG tube.
Other instructions:
When to call the healthcare provider
Call the healthcare provider right away if your child has any of these:
-
Redness, swelling, leakage, sores, or pus on the skin around the tube site
-
Blood around the tube, or in your child’s stool or vomit
-
Coughing or vomiting while feeding
-
Vomiting between feedings
-
Belly that looks bloated or feels hard when gently pressed
-
Diarrhea or constipation
-
Fever 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as advised by the provider
Call 911
Call 911 if your child has trouble breathing or is choking during feeding or flushing.